Understanding Cataracts
A cataract is a clouding of the eye's natural lens, which lies behind the iris and the pupil. Cataracts are the most common cause of vision loss in people over age 40 and are the principal cause of blindness worldwide. In fact, there are more cases of cataracts worldwide than there are of glaucoma, macular degeneration, and diabetic retinopathy combined.
Common Symptoms of Cataracts
- Cloudy, blurry, or dim vision
- Increasing difficulty with vision at night
- Sensitivity to light and glare
- Need for brighter light for reading and other activities
- Seeing "halos" around lights
- Frequent changes in eyeglass or contact lens prescription
- Fading or yellowing of colors
- Double vision in a single eye
When is Surgery Needed?
Cataract surgery is recommended when cataracts begin to affect your quality of life or interfere with your ability to perform normal daily activities, such as reading, driving, or watching television. The decision to have surgery is a personal one that you should make in consultation with your ophthalmologist.
Cataracts typically develop slowly and painlessly. Many people don't realize they have cataracts until their vision is significantly impaired. Regular eye exams are essential for early detection.
Our Cataract Surgery Procedure
Modern, minimally invasive techniques for optimal results
Pre-Surgical Evaluation
Before surgery, we conduct a comprehensive eye examination to measure the size and shape of your eye. This helps us determine the right type of intraocular lens (IOL) for your specific needs.
Visual acuity test, eye pressure measurement, corneal topography, and IOL power calculation.
Day of Surgery
Cataract surgery is an outpatient procedure that typically takes less than 30 minutes. Your eye will be numbed with drops or local anesthesia, and you'll remain awake but relaxed during the procedure.
Arrive 1-2 hours before surgery, wear comfortable clothing, and arrange for someone to drive you home afterward.
Surgical Procedure
We use phacoemulsification, a modern technique that requires only a tiny incision. Ultrasound energy breaks up the cloudy lens, which is then removed by suction. A clear artificial lens is inserted to replace the natural lens.
The procedure is painless, and most patients report only mild pressure sensations. The small incision typically heals on its own without stitches.
Recovery and Follow-up
Most patients notice improved vision within a few days. Complete healing may take several weeks. We'll schedule follow-up appointments to monitor your progress and ensure optimal healing.
You'll use prescribed eye drops, avoid strenuous activities for a week, and protect your eye from bright light and potential irritants.
Intraocular Lens Options
Choose the lens that best fits your lifestyle and visual needs
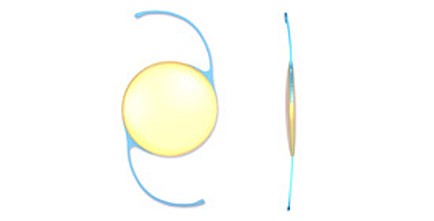
Monofocal Intraocular Lenses
Standard single-focus lens typically set for distance vision. Most commonly used lens type that provides clear vision at one fixed distance.

Monofocal Toric Intraocular Lenses
Single-focus lens with built-in astigmatism correction. Provides clearer vision for patients with corneal astigmatism.

Trifocal Intraocular Lenses
Advanced lens with three focal points for near, intermediate, and distance vision. Provides a full range of vision without glasses.

Trifocal Toric Intraocular Lenses
Premium lens combining trifocal technology with astigmatism correction. Ideal for patients with astigmatism seeking spectacle independence.
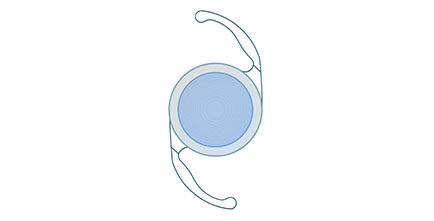
Multifocal Intraocular Lenses
Advanced lens design with multiple focus points. Allows patients to see clearly at various distances without glasses.

Multifocal Toric Intraocular Lenses
Combines multifocal technology with astigmatism correction. Provides clear vision at multiple distances for patients with astigmatism.

Extended Depth Of Focus (EDOF) Intraocular Lenses
Extended Depth of Focus lens provides a continuous range of vision. Offers excellent distance and intermediate vision with functional near vision.
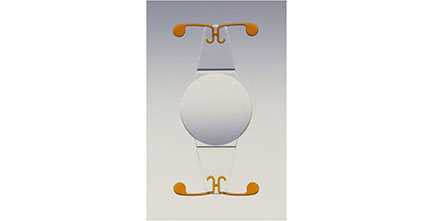
Accommodative Intraocular Lenses
Innovative lens that moves or changes shape within the eye. Mimics the natural focusing ability of the young crystalline lens.
Lens Comparison
| Lens Type | Distance Vision | Intermediate Vision | Near Vision | Astigmatism Correction | Glasses Independence (Distance) | Glasses Independence (Near) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monofocal IOL | ★★★★★ | ★★☆☆☆ | ★☆☆☆☆ | ❌ | ❌ | ✔️ |
| Monofocal Toric IOL | ★★★★★ | ★★☆☆☆ | ★☆☆☆☆ | ✔️ | ❌ | ✔️ |
| Trifocal IOL | ★★★★★ | ★★★★★ | ★★★★★ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Trifocal Toric IOL | ★★★★★ | ★★★★★ | ★★★★★ | ✔️ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Multifocal IOL | ★★★★☆ | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★☆ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Multifocal Toric IOL | ★★★★☆ | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★☆ | ✔️ | ❌ | ❌ |
| EDOF IOL | ★★★★★ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★☆☆ | ❌ | ❌ | ✔️ |
| Accommodative IOL | ★★★★★ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★★ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |